Understanding Natural Killer (NK) Cells: Immune System Defenders
1) Natural killer cells (NK)
Natural killer cells (NK) are important immune cells in the body that function as an anti-tumor, anti-viral infection and immune regulation as well as participating in hypersensitivity and autoimmune diseases functions.
The origin source of NK cells is not well understood and is generally thought to be derived directly from the bone marrow, which is dependent on the microenvironment of the bone marrow. In vitro experiments in mice and humans have shown that lymocytes can also induce NK cells by culturing in the presence of IL-2 and other cytokines in vitro. Mouse spleen can promote the differentiation of NK cells induced by IL-3 in vivo. NK cells are mainly distributed in peripheral blood, accounting for 5- 10% of PBMC. There are also NK activities in lymph nodes and bone marrow, but at a level lower than that of peripheral blood.
The specificity of NK cell surface markers is relative to T cells and B cells. Human NK cells mIg-, part of NK cells positive for CD2, CD3 and CD8, express IL-2 receptor β chain (P75, CD122), CD11b/CD18 positive. Commonly used markers for detecting NK cells are CD16, CD56, CD57, CD59, CD11b, CD94 and LAK-1. Study have been demonstrated that NK cells have partial T cell differentiation antigens, such as 80~90% NK cells CD2+, 20~30% NK cells CD3+ (expressing CD3 δ chain), 30% NK cells CD8+ (α/α) and 75~90% NK cells CD38+. Since, NK cells have IL-2 receptor, therefore, NK proliferation can be stimulated by IL-2, and activated NK cells can secrete cytokine IFN-γ, hence, NK cells are considered to be more closely related to T cells.
Interested in learning more about NK cells and their role in the immune system? Contact us for in-depth information and professional insights
2) Recognition of NK cell to target cell
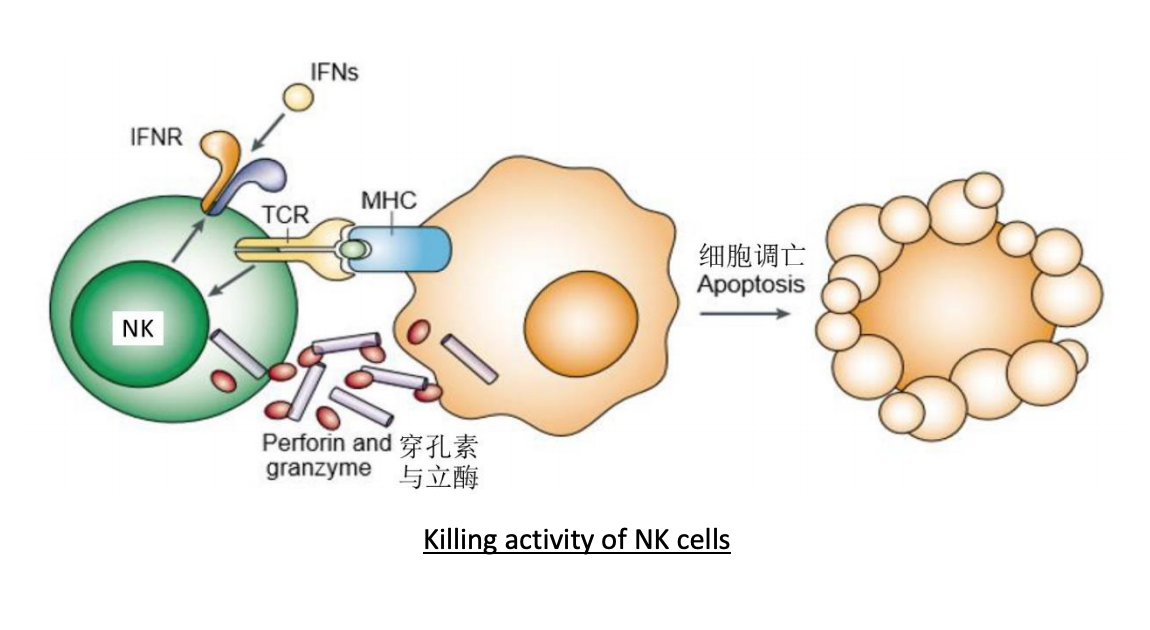
Since the killing activity of NK cells is not restricted by MHC and is not dependent on antibodies, it is called natural killing activity. Cytoplasm of NK cells contain large azurophilic granules that have spontaneous cytotoxicity against a variety of tumor cells, virus-infected cells, and some normal cells in the bone marrow and thymus.
Identifying target cells NK cells recognize that target cells are non-specific, however, it is unclear that how the NK cell recognize a target cells. It is plausible that lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) interacts with the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) on the surface of target cells to participate in the recognition process of NK cells. In addition, binding of CD2 to LFA-3 (CD58) and CD56 may also mediate binding of NK cells to target cells.
Have questions about NK cell recognition processes? Our experts are here to provide the answers. Get in touch with us today!
3) Mechanism of cytotoxic effect of NK cell
(1) NK cell contain perforin. Perforin is a pore-forming protein that leads to osmotic lysis of the target cells and subsequently enables granzymes to enter the target cells and activate apoptosis, the cell death program.
(2) NK cytotoxic factor: NK cells can release soluble NK cytotoxic factor (NKCF), and NKCF receptor is on the surface of target cells. NKCF can selectively kill and lyse target cells after binding to target cells.
(3) Tumour necrosis factor (TNF): activated NK cells can release TNF-α and TNF-β (LT), TNF can change the stability of target cell through lysosome and lead to leakage of various hydrolase; affect cell membrane phospholipid metabolism; change target cells Glucose metabolism reduces the pH in the tissue and activates the target cell endonuclease, degrades the genomic DNA to cause programmed cell death and other mechanisms to kill the target cells. The process of TNF-induced cell death is significantly slower than that of perforin-dissolving cells.
(4) Secreted cytokines: Activated NK cells can synthesize and secrete a variety of
cytokines, play a role in regulating immune and hematopoietic effects and directly killing target cells.
For more click here.
For a deeper dive into the cytotoxic mechanisms of NK cells and their therapeutic potential, reach out to our team for detailed discussions and professional guidance.
Key Biomarkers for Heart Health: The 4 Blood Tests You Shouldn't Skip
Key Biomarkers for Heart Health: The 4 Blood Tests You Shouldn't Skip
- Omega-3 Index
- CRP (C-Reactive Protein)
- Insulin
- Triglyceride/HDL ratio
Omega-3 index
The omega-3 index is defined as the amount of EPA plus DHA in red blood cell (RBC) membranes expressed as the percent of total RBC membrane fatty acids. The EPA + DHA content of RBCs correlates with that of cardiac muscle cells, and several observational studies indicate that a lower omega-3 index is associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) mortality. It is therefore proposed that the omega-3 index be used as a biomarker for cardiovascular disease risk, with proposed zones as below:
Acceptable Omega-3 Levels:
- Lower risk = 8% or higher
- Medium risk = 4 to 8%
- Higher risk = under 4%
The real gems in the results may be the level of Omega-6 Arachidonic Acid (AA/EPA ratio) in your cell membranes and your Omega-6 to 3 ratio.
It is easy to boost your Omega-3 index quickly by eating fish or taking fish oil supplements. But the equally important job of decreasing Omega-6 is a very slow process and requires eliminating vegetable seed oils and reducing nuts, seeds and poultry.
You can get your Omega-3 index measured at Eternal Clinic & Wellness, Rxidence Compounding located at Puchong, Selangor (03-80711800), Pure Health Pharmacy located at Bukit Mertajam, Penang and Sunrise Homecare Pharmacy located Bayan Lepas, Penang.
Concerned about your heart health? Contact us to learn how you can get your Omega-3 index and other vital health markers measured accurately.
2. CRP (C-Reactive Protein)
C-Reactive Protein is an indicator of inflammation. CRP is released from the liver in response to inflammation.
Why you should care: it is a good predictor of future cardiac events in people who are currently healthy. C-Reactive Protein and relative risk of first heart attack. People with the highest CRP have a 4-fold increased risk for heart attacks.
We didn’t know the predictive ability of CRP until 1997. CRP does not point to the presence of a specific disease, but inflammation is closely tied to several diseases.
Chronic inflammation of cardiac tissues and endothelium are hallmarks of poor heart health. The scar tissue from this inflammation is one of the early drivers of plaque build up.
People with high CRP are up to 4 times more likely to have cardiac events and at 4 to 6 times greater risk of developing diabetes.
It’s actually a much better predictor of heart health and stroke than LDL ‘bad’ Cholesterol.
Acceptable CRP Levels:
• Lower risk: less than 1.0 mg/L • Average risk: 1.0 to 3.0 mg/L • Higher risk: above 3.0 mg/L • Above 10 mg/mL usually indicates acute inflammation
It’s important to order the High-sensitivity CRP or hs-CRP test. The regular CRP test measures down to 3 mg/L whereas hs-CRP measures down to 0.3 mg/L, allowing you to detect low levels of chronic inflammation.
There are no drugs approved for lowering CRP, but some statins lower it. Several other Rx drugs lower it too, but all have significant side effects.
High CRP is a bright neon sign over your head saying ‘Time for lifestyle change.’
Diet and lifestyle factors like exercise, eating an anti-inflammatory diet (Zone, Paleo etc.), healing your gut, lowering sugar/Omega-6 can lower CRP. Using all the techniques above, I managed to get my CRP down from almost 4 to under 0.3.*
Talk to your doctor about adding this test to your panel and techniques for lowering it.
Elevated CRP levels? Speak with our specialists for personalized advice on reducing inflammation. Get in touch today.
3. Insulin
Insulin is the hormone that manages your blood sugar levels and your fat metabolism.
Insulin spikes and falls based on what you eat.
Your blood has very little capacity to contain sugar. So, if you drink a glass of soda or orange juice, you’ve consumed way more sugar than what your body was built for. Excess blood sugar can give you a mild case of coma or death. To keep you from going into coma, your pancreas cranks out insulin.
Insulin then lowers your blood sugar back to safe levels. The down side? The sugar gets packed away as fat. Every time you drink a glass of orange juice, your body shifts silently to ‘Defcon 5’ and back without you knowing it.
Why you should care: 8 out of 10 people with heart attacks also have high insulin. High insulin is a hallmark of metabolic syndrome.
A diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates will keep your insulin levels high. This leads to weight gain, high triglycerides, low HDL and small/dense variety of LDL cholesterol.
In people prone to the problem, a diet that’s consistently high in insulin-elevating sugars and carbs will lead to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition where the body ‘gives up’ and stops responding to higher and higher levels of insulin produced by the pancreas.
Like CRP, high post-prandial (after a meal) insulin levels can predict your likelihood of developing insulin resistance, pre-diabetes and diabetes. It’s easier to get your fasting insulin measured and that’s very useful too.
Measuring your fasting insulin along with your regular lipid panel is easy and your doctor ought to test it.
Acceptable Fasting Insulin Levels: Aim for 4 uIU/ml or lower. The average American is above 8.
Reducing sugar, juice, soda, grains and refined carb consumption is the best way to prevent high insulin levels. The diabetes drug metformin can reduce it. And, yes, exercise has a positive impact.
The good news: if you’re still young and/or undamaged from years of unlimited carb-feasting, going on a restricted diet like the paleo diet may drop your insulin levels quickly. In a pig study, Paleo diet dropped insulin in as little as 10 days. A few people I know fit the description, so thought I’d share. Your mileage, obviously, will widely vary.
Low-carb diets have also been shown to bring high insulin under control.
I was able to drop my sky-high insulin level down to the normal range by going on a low-carb, high-veggie paleo type diet with daily exercise. If I go on vacation and eat gelato or flan every day (Pshaw – who would do such a thing?!), my insulin (and love handles) return. Quickly. And then I look like this guy.
Struggling with insulin management? Our team can help. Schedule a consultation to discuss effective strategies for maintaining healthy insulin levels.
4. Triglyceride (TG)/HDL Ratio
Ok – this is not an actual test. Your regular lipid panel already has your Triglyceride (TG) and HDL numbers.
By dividing the Triglyceride number by the HDL you get a ratio that is very informative.
Why you should care: People with the highest TG/HDL levels are 16 times more likely to suffer a heart attack.
Triglyceride to HDL ratio is a reliable predictor of heart attacks. People with the highest levels are 16-times more likely to suffer heart attacks than those with the lowest.
Calculating this ratio is a simple trick to measure your risk for insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, pre-diabetes, LDL particle size and, of course, poor heart health.
High triglyceride and low HDL levels are independently good at predicting atherosclerosis. When you combine these two readily available data points, you are looking into your future with a telescope.
Small dense LDL particles are more dangerous than large ones. Measuring LDL particle density is somewhat expensive, but your TG/HDL ratio is also a poor man’s LDL density predictor. If your ratio is above 3.8, you have an 80% chance of having the more dangerous small, dense LDL. And with a ratio of less than 3.8, you have 80% likelihood of having the large, less dangerous LDL.
TG/HDL Levels:
If your TG/HDL ratio is less than 1, you are at lower risk. 1 to 3 represents medium risk. 3 or higher may mean that you are at high risk and insulin resistant.
This ratio cuts through the confusion about ‘cholesterol numbers.’
We’ve only known about this since the turn of the century, so most doctors and lab tests don’t focus on it, even though it may be the strongest predictor of heart attack on your lipid panel.
Is it hard to get this ratio down? Yes. Mine was a sky-high 17 a few years ago. I got it down to 2.5. I’ve written about my struggles and eventual success in getting my triglyceride levels down, here and here. Simply put, it involves reducing or cutting out sugar, sodas, juices, fruits and grains.
Drugs like Lovaza can help reduce triglyceride. So can Metformin.
A low-fat, high whole-grain diet will almost certainly not work. In fact, that’s what got my ratio up to 17.
Smoking, trans fats, Omega-6 fats and fructose can all decrease HDL.
Low-carb diets are more effective than low-fat diet at getting this ratio down.
Raising HDL is harder and slower – increasing exercise, not sitting a lot, increasing healthy fats all help. Advanced HDL-boosting techniques like ketogenic diets and intermittent fasting can also help, but it will require the assistance of a professional nutritionist.
Besides these four measures, homocysteine, apoB, ferritin, coronary calcium score, and oxLDL are also good predictors of heart health. More on those another day.
Want to improve your TG/HDL ratio? Our nutrition experts can guide you. Contact us for a tailored diet plan.
An Overview: Omega 3 Index Complete Test
Maximizing Wellness: A Deep Dive into the Omega-3 Index and Cellular Inflammation Testing
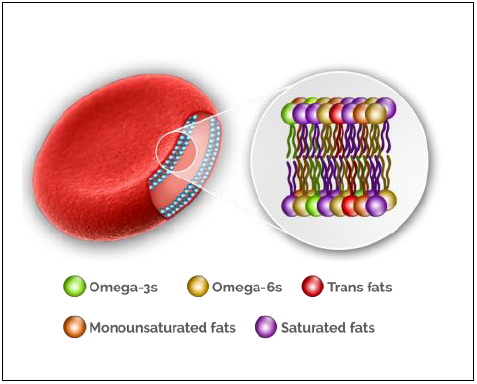
The Omega-3 Index Complete Test also known as cellullar inflamation testing. It gives you a snapshot of the fats that make up our cells. The test measures the following:
- AA / EPA ratio
- Omega-3s
- Omega-6s
- Saturated fats
- Monounsaturated fats
- Trans fats
- Omega 3/ Omega 6 ratio
Cellular Inflammation: The Silent Disruptor
Often undetectable by pain, cellular inflammation works covertly, disrupting hormonal signals at the cellular level. This can lead to increased fat storage, hastened onset of chronic diseases, and reduced physical performance. Although invisible, its presence is measurable through the Omega-3 Index, specifically by evaluating the AA/EPA ratio in your bloodstream.
Decoding the AA/EPA Ratio
The AA/EPA ratio is a direct indicator of cellular inflammation within your body. While a high ratio doesn’t necessarily indicate disease, it does suggest that your wellness could be optimized. The Omega-3 Index reflects this ratio, and studies, including notable research from Italy, have linked a ratio above 15 to an increased risk of chronic conditions.
AA/EPA Ranges
1.5 to 3
3 to 6
7 to 15
> than 15
Cellular Inflammation
Low
Moderate
Elevated
High
Future state of wellness
Excellent
Good
Moderate
Poor
Dietary Strategies to Optimize Your Omega-3 Index
Pharmaceutical interventions cannot alter the AA/EPA ratio; only dietary changes can. To improve your Omega-3 Index, consider increasing your intake of high-purity omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA. This adjustment can swiftly lower the AA/EPA ratio. For long-term maintenance, a diet low in inflammatory foods—like the Zone, Ketogenic, or Paleo diets—can help sustain a healthy Omega-3 Index and reduce cellular inflammation.
EPA and DHA Intake: Tailoring Your Diet for Cellular Health
How much EPA and DHA is necessary to maintain a favorable Omega-3 Index? Research suggests a daily intake of 2.5 grams for individuals at risk for conditions like breast cancer. This dosage aligns with findings from Italian studies, where patients with chronic diseases and high AA/EPA ratios experienced significant improvements with consistent EPA and DHA supplementation. For personalized guidance, regular blood tests can help adjust your EPA and DHA intake to optimize your Omega-3 Index.
Grams of EPA and DHA supplemented per day
0
0.8
2.5
5.0
7.5
AA/EPA Ratio
12.1
4.7
2.6
1.3
1.2
This data indicates that a daily dosage of EPA and DHA of 2.5 grams was sufficient to bring the AA/EPA ratio into the desired range for excellent wellness for these healthy individuals. This level of EPA and DHA recommendation correlates well with an Italian study that demonstrated in patients with various chronic diseases having an elevated AA/EPA ratio (>15) lowered their elevated AA/EPA ratio to approximately 5 with daily supplementation of 2.5 grams of EPA and DHA. This is also indicative that a person with an existing chronic disease may need greater amounts of EPA and DHA to get them into an excellent wellness range compared to a healthy individual. Updated on 6 Aug 2019
However, these are only general guidelines for daily EPA and DHA supplementation. The best indication of the amount of EPA and DHA required to optimize the AA/EPA ratio for an individual is best determined with blood testing every six to twelve months.
Omega 3
The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is found mainly in plant oils such as flaxseeds, walnuts, and their oils are among the richest dietary sources of ALA. Canola oil is also an excellent source of ALA. Dietary surveys in the US indicate that average adult intakes for ALA range from 1.8-2.0 g/day for men and from 1.4-1.5 g/day for women.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): Oily fish are the major dietary source of EPA and DHA. Dietary surveys in the US indicate that average adult intakes of EPA range from 0.03-0.06 g/day, and average adult intakes of DHA range from 0.05-0.10 g/day.
Humans can synthesize arachidonic acid(AA) from LA and EPA and DHA from ALA through a series of desaturation and elongation reactions. EPA and DPA are also obtained from the retroconversion of DHA. Due to low conversion efficiency, it is advised to obtain EPA and DHA from additional sources.
Omega-3s are important components of the membranes that surround each cell in your body. DHA levels are especially high in retina (eye), brain, and sperm cells. Omega-3s also provide calories to give your body energy and have many functions in your heart, blood vessels, brain, eye, lungs, immune system, and endocrine system (the network of hormone-producing glands). There are multiple benefits to the mind and body in having a higher Omega-3 Index, all of which contribute to slower aging.
Omega 6
Like omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids.
These fats are primarily used for energy. The most common omega-6 fat is linoleic acid. Linoleic acid itself plays a special role in support of heart health. It reduces total and LDL cholesterol, improves insulin sensitivity and blood pressure.
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) is an omega-6 fatty acid found in certain oils, such as evening primrose oil and borage oil. It can reduce a number of symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is another form of omega-6 fat that has some health benefits. It reduces body fat mass. Updated on 6 Aug 2019
Saturated Fat
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all or predominantly single bonds. Examples of foods containing a high proportion of saturated fat include animal fat products such as cream, cheese, butter, other whole milk dairy products and fatty meats which also contain dietary cholesterol. The World Health Organization, have advocated for reduction in the intake of saturated fat to promote health and reduce the risk from cardiovascular diseases.
Monounsaturated fat
Monounsaturated fat is a type of dietary fat. It is one of the healthy fats, along with polyunsaturated fat. Monounsaturated fats are found in plant foods, such as nuts, avocados, vegetable oils, olive oil, sesame oils. Foods containing monounsaturated fats reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, while possibly increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Monounsaturated fats help develop and maintain your cells.
Trans fats
There are two broad types of trans fats found in foods: naturally-occurring and artificial trans fats. Naturally-occurring trans fats are produced in the gut of some animals and foods made from these animals (e.g., milk and meat products) may contain small quantities of these fats. Artificial trans fats (or trans fatty acids) are created in an industrial process that adds hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils to make them more solid.
The primary dietary source for trans fats in processed food is “partially hydrogenated oils.”
Trans fats can be found in many foods – including fried foods like doughnuts, and baked goods including cakes, pie crusts, biscuits, frozen pizza, cookies, crackers, and stick margarines and other spreads.
Why OmegaQuant Omega 3 Complete Test Kit?
- It is the world’s only laboratory dedicated to fatty acid analysis that is CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments) certified and regulated by FDA.
- This test has been used in 200+ research studies
- Validated and standardised testing methods by FDA
- OmegaQuant is a recognised expert in fatty acid research
Naltrexone Overview: Benefits, Uses, and Safety | Eternal Wellness
Naltrexone
 Naltrexone is in a class of medication known as opioid receptor antagonist. It works by blocking the effects of narcotic drugs and is used to prevent substance abuse in people who have been addicted to alcohol or opioid pain medications. In addition to the antagonist effect on opioid receptors, naltrexone simultaneously has an antagonist effect on non-opioid receptors. It is via the non-opioid antagonist path that Naltrexone at low dose (LDN) is thought to exert its anti-inflammatory effects. Basic science evidence supports that concept by showing that low- and high-dose opioid antagonists have quite different impacts on the physiologic system. As a rule of thumb, low dose would range from 0.5 to 4.5 mg daily.
Naltrexone is in a class of medication known as opioid receptor antagonist. It works by blocking the effects of narcotic drugs and is used to prevent substance abuse in people who have been addicted to alcohol or opioid pain medications. In addition to the antagonist effect on opioid receptors, naltrexone simultaneously has an antagonist effect on non-opioid receptors. It is via the non-opioid antagonist path that Naltrexone at low dose (LDN) is thought to exert its anti-inflammatory effects. Basic science evidence supports that concept by showing that low- and high-dose opioid antagonists have quite different impacts on the physiologic system. As a rule of thumb, low dose would range from 0.5 to 4.5 mg daily.
Naltrexone is almost completely absorbed (96%), but its oral bioavailability ranges between 5% and 40% due to first-pass metabolism.
Benefits
Use of low dose naltrexone (LDN) for inflammatory diseases, fibromyalgia, neurological conditions, cancer and mood disorders
Low doses of naltrexone have been shown to reduce symptom severity in:
 multiple sclerosis
multiple sclerosis- fibromyalgia
- Crohn’s disease
- cancer
- complex regional pain syndrome, and other chronic pain disorders.
- depression
Use of LDN for Weight Loss
LDN can help balance the emotional hormones in your body (such as reversing low dopamin’s effects), thereby reducing your desire to snack out of anxiety. It also helps curb your cravings through an appetite-suppressant effect that helps you feel full for longer periods of time.
Use in Sleep disorders
Naltrexone has been shown to help improve sleeping patterns significantly in patients with sleep apnea.
Active Ingredient : Naltrexone 1.5mg
Product Form : Capsules – 30 caps
Recommended Dosage
- For Pain Management and inflammatory diseases : Typically 0.5 mg at bedtime for several weeks, followed by 0.5 to 1.0 mg incremental increases over a 1- to 3-month period up to the maximum dose of 4.5mg.
If a patient is at the typical maximum dose of 4.5 mg and symptoms return, the clinician should consider reducing or discontinuing LDN for 1 to 2 weeks, then reinitiating medication at a lower dose and building back up to a maximum effective dosage. When inflammatory markers are used to diagnose or follow a patient’s progress (eg, ESR, CRP) it is important to track these levels and correlate them with changes in symptomatology. - Weight Loss & Sleep Disorders : 1.5 to 4.5mg per day preferably at bedtime. If patients report nightmares then take the dose in the morning with or without food. Can be used in combination with hormone therapies, nutrients/supplements and dietary/lifestyle changes.
- Depression : 1 mg 2 times a day for 2 weeks at bedtime.
Contraindications and interactions
Naltrexone is contraindicated for known drug allergy and in hepatitis and kidney disorder patients.
Side effects and Special Precautions
- Can cause liver damage if taken in doses larger than what is recommended.
- Vivid dreams which decreases after a few nights
- Headache, dizziness or drowsiness
- Stomach pain or cramping
- Treats fibromyalgia, endometriosis and uterine fibroids.
- Naltrexone shouldn't be used by people who are still using opioids or drinking large amount of alcohol or who are currently experiencing withdrawal syndromes.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Naltrexone might harm an unborn baby. There is not enough reliable information about the safety of taking Naltrexone during breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
What G6PD-deficient individuals should really avoid
What G6PD-deficient individuals should really avoid
G6PD Deficiency Food To Avoid
Some of the foods commonly eaten around the world can cause people with G6PD Deficiency to hemolyze. Some of these foods can be deadly (like fava beans). Some others can cause low level hemolysis, which means that red blood cells die, but not enough to cause the person to go to the hospital. Low level hemolysis over time can cause other problems, such as memory dysfunction, over worked spleen, liver and heart, and iron overload. Even though a G6PD Deficient person may not have a crises when consuming these foods, they should be avoided.
Fava beans and other legumes
This list contains every legumes we could find, but there may be other names for them that we do not know about. Low level hemolysis is very hard to detect and can cause other problems, so we recommend the avoidance of all legumes.
Sulfites
And foods containing them. Sulfites are used in a wide variety of foods, so be sure to check labels carefully.
Menthol
And foods containing it. This can be difficult to avoid as toothpaste, candy, breath mints, mouth wash and many other products have menthol added to them. Mint from natural mint oils is alright to consume.
Artificial blue food coloring
Other artificial food color can also cause hemolysis. Natural food color such as found in foods like turmeric or grapes is okay.
Ascorbic acid
Artificial ascorbic acid commonly put in food and vitamins can cause hemolysis in large doses and should be avoided. It is put into so many foods that you can be getting a lot of Ascorbic Acid without realizing it. See Ascorbic acid for more information about iron absorption and ascorbic acid.
Vitamin K
This is from drugbank: “Menadione (Vitamin K3), which is not used as a nutritional supplemental form of vitamin K for humans, has been reported to cause adverse reactions, including hemolytic anemia. Large doses have also been reported to cause brain damage. Vitamin K administered to newborns with G6PD Deficiency has been known to cause adverse outcomes including hemolytic anemia, neonatal brain or liver damage, or neonatal death in some cases.
Tonic water
(contains quinine, a contraindicated drug which causes hemolysis in G6PDD people)
Bitter Gourd and Garden Egg
Bitter Gourd is also known as Bitter Mellon. These are common foods in some parts of Africa and Asia.
Some Chinese Herbs
Particularly Rhizoma Coptidis (huang lien), Calculus Bovis (neu huang), Flos Chimonanthi Praecocis (leh mei hua), Flos Lonicerae (kam ngan fa) and Margarita or anything containing them.
List of Legumes for Those With Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Deficiency and Favism
Fava beans are contraindicated for people with G6PD Deficiency, however, many people also react to varying degrees to many or all legumes. Many times the reaction is not a full blown hemolysis where hospitalization is required, but does cause hemolysis of a lesser degree. Over time, these smaller hemolysis events can lead to other more serious complications or related disorders. See Why We Recommend Avoiding Legumes for more information. The list is provided as an aid to those wishing to abstain from all legumes. If you would like more information about legumes and g6pd deficiency, Plants Of Life, Plants of Death has in interesting discussion.
Beans
aduiki bean
adzuki bean
anasazi beans
appaloose bean
asuki bean
azufrado bean
azuki bean
baby lima bean
bayo bean
bengal bean
black azuki bean
black bean
black turtle bean
bolita bean
bonavist bean
borlotti bean
Boston bean
Boston navy bean
broad bean
brown speckled cow bean
buffalo bean
butter bean
butterscotch calypso bean
calypso bean
canaria bean
Madagascar bean
maicoba bearn
maine Yellow eye
mayocoba bean
marrow bean
mauritius bean
Mexican black bean
Mexican read bean
molasses face bean
mortgage lifter bean
mortgage runner bean
moth dal
mucuna bean
mucuna pruriens
mucuna prurita
mung bean
mung pea
mungo bean
navy bean
nescafe
orca bean
pea bean
pearl haricot
Peruano bean
Peruvian bean
Canario bean
Cannellini bean
Chestnut lima bean
Chili bean
Christmas lima bean
Cabeca-de-frade
Chiporro
Coco bean-French white bean
Coco blanc bean-French white bean
Crab eye bean
Couhage
Cowage
Cowhage
Cowitch
Cranberry bean
Dermosan bean
Dolichos pruriens
Edamame
Egyptian bean
Egyptian white broad bean
English bean
European soldier bean
Eye of the goat bean
Faba
Fagiolo romano
Fava bean
Fava-coceira
Fayot
Fazolia bean
Feijao bean
Feve
Field pea
Flageolet
Fool
Foul
Frijo bola roja
Frijole negro
Fuji mame
Ful
Great northern bean
Green gram
Haba
Habas
haricot blanc bean
Horse bean
Hyacinth bean
Itchy bean
Indian bean
Jackson wonder bean
Jacob’s cattle bean
Krame
Kidney bean
lablab bean
picapica
pink bean
pinto bean
po de mico
prince bean
purple appaloosa bean
rajma
rattlesnake bean
red ball bean
red bean
red eye bean
red chori
red kidney bean
red oriental bean
rice bean
rosecoco bean
roman bean
runner bean
saluggia
salugia bean
scarlet runner bean
setae siliquae hirsutae
shell bean
small red bean
small white bean
soy bean
soya bean
soybean
Spanish black bean
Spanish tolosana ben
Specked brown cow bean
Steuben yellow bean
Steuben yellow eye bean
Stizolobium pruriens
Sweet bean
Swedish brown bean
Tapary bean
Tepary bean
Tiensin red bean
Tolosana bean
Tongues of fire bean
Tremmocos
Trout bean
Turtle ben
Turtle soup bean
Vallarta bean
Val
Velvet bean
Wax bean
Shit bean
White kidney bean
White pea bean
Windsor bean
Lima bean
Lingot bean
Lupini bean
Yankee bean
Yellow Indian woman bean
Yin yang bean
Snap Beans
Asparagus bean
Asparagus pea
Bodi
Boonchi
Chepil
Chinese long bean
Dau gok
Dow gok
Dragon tongue bean
French bean
French green bean
Four-angled bean
Goa bean
Green bean
Haricot verts
Italian flat bean
Long bean
Manila bean
Princess pea
Romano bean
Runner bean
Sator
Snap bean
String bean
Thailand long bean
Wax bean
Winged bean
Winged pea
Yard-long bean
Edible Pods
Chinese pea pod
Chinese pea
Chinese snow pea
Edible-podded pea
Mange-tout pea
Snow pea
Sugar pea
Sugar snap
Bean products
Black beans in salted sauce
Black salted fermented bean
Chinese black bean
Dow see
Fermented black bean
Frijoles refritos
Refried beans
Salted black bean
Salty black bean
Lentils
Arhar
Arhar dal
Beluga black lentil
Beluga bentil
Bengal gram
Black beluga lentil
Black chickpeas
Black gram
Black lentil
Lablab beans
Lentils du Puy
Lentils vertes du Puy
Masar
masar dal
masoor
massor dal
matki
moath
Brown lentil
Channa dal
Chana dal
Chilke urad
Chowli dal
Continental lentil
Dal / Daal / Dhal / Dhall
Egyptian lentil
French green lentils
German lentil
Gram dal
Green lentil
Horse gram
Indian brown lentil
Kala channa
Kali dal
Moong dal
Mussoor
Mussor dal
Petite beluga lentil
Puy lentil
Red lentil
Toor
Toor dal
Tuvar dal
Tur
Tur dal
Urad dal
Val dal
White lentil
Yellow lentil
Peas
Bengal gram
Black-eyed pea
Black-eye bean
Black-eye pea
Black-eyed suzy
Ceci bean
Cici bean
China bean
Chawli
Chickpea
Chick-pea
Chole
Congo pea
Congo bean
Cowpea
Crowder pea
Dried peas
Egyptian pea
Field peas
Fresh peas
Gandules
Garbanzo bean
Garbanzo pea
Garbonzo bean
Gongoo pea
Green pea
Green matar dal
Green split pea
Gunga pea
Kabuli channa
Kabli chana
Kabli channa
Lobhia
Locust bean
Lombia
No-eyed peas
Pigeon pea
Posi chiches
Poor man’s pea
Southern pea
White chickpea
Yellow pea
Yellow matar dal
Yellow-eyed pea
Gungo pea
Soy Products
Abura-age
Aburage
Aka miso
Akamiso
Atsi-age
Atsuage
Bamboo yuba
Barley miso
Awase miso
Bean cheese
Bean curd
Bean curd sheets
Bean curd skins
Bean curd stick
Bean paste
Bean sauce
Bean stick
Brown rice miso
Chinese yuba
Dark miso
Deep fat fried tofu
Deep-fried tofu
Doufu
Dow fu kon
Dried bean curd stick
Dried bean stick
Extra-firm tofu
Fermented bean cake
Fermented bean curd
Fermented soy cheese
Firm tofu
Foo yu
Fried bean curd
Fu jook pei
Fu yi
Fu yu
Genmai miso
Hat-cho miso
Inaka miso
Imariage
Kinu-goshi
Kirazu
Kyoto shiro miso
Mame miso
Medium tofu
Mellow white miso
Miso
Mugi miso
Nama-age
Nama mori san
Nato
Natto
Nattou
Nigari tofu
Okara
Plant protein
Preserved bean curd
Pressed tofu
Protein crumbles
Red miso
Regular tofu
Roasted soybeans
Sendai miso
Shinshu miso
shiro miso
silken tofu
soft tofu
spy cheese
spu mayonnaise
soy milk
soy milk skins
soy sour cream
soy nuts
soy yogurt
soya cheese
soya mayonnaise
soybean curd
soybean paper
soybean paste
soynuts
soy nut butter
sui-doufu
sweet miso
sweet white miso
tempeh
textured soy protein
Textured vegetable protein
Tofu
Tofu mayonnaise
Tofu sour cream
TSP
TVP
uba
unohana
usu-age
ususage
vegetable protein
wet bean curd
white miso
yellow miso
yuba
Vegetable Gum Thickeners
These are either made from legumes, or can be made from legumes
Albumin – from peas
Acacia gum
Carob bean gum
Flavoring or natural flavoring
Gum Arabic
Guar gum
Lecithin
Locust bean gum
Monosodium glutamate (from soy)
Tara seed gum
Tragacanth
Vegetable broth (soy or even fava beans)
Vegetable emulsifier
Vegetable glycerin
Vegetable gelatin
Vegetable stabilizer
Other Legumes
Alfalfa sprouts
Astragalus (herbal medicine)
Carob (chocolate substitute)
Fenugreek
Jicama
Licorice
Peanuts
Rooibos
Red Tea
African Red Tea
Senna or Cassia
Singkamas
Tamarind
Vetch family (Not normally used for
food)
Other Foods Likely to Contain Hidden Soy or Legume Additives
Artificial butter flavor
Baked goods
Candies
Canned meats or tuna
Canned soups
Chips
Chinese food
Gravy mixes
Infant formula
Low fat cheeses or cheese substitutes
Margarine
Sausages, hot dogs, processed meats
Sauces (Worcestshire. Sweet and Sour etc)
Salad Dressings
Stock or bouillon
Tofutti
Powdered foods
Why We Recommend Avoiding Legumes
There is a lot of controversy about legumes causing hemolysis in G6PD Deficient patients. In order to address this issue, I will first address the issue of varying degrees of hemolysis
Low level hemolysis
Most doctors and other medical professionals see hemolysis in G6PDD patients as an all or nothing problem. If you don’t hemolyze badly enough to send you to the hospital, you’re fine. I strongly disagree with this for the following reasons:
- If that were true, all hemolytic events would end in death, and this is not correct. The vast majority of hemolytic events are mild enough for the body to compensate for without intervention. Following this reasoning, it is only logical that hemolysis can happen from very mild to very severe, depending on circumstances such as health, stress, trigger, age, etc.
- Many people go for years experiencing hemolysis without knowing it. They can have other health issues that eventually lead to the discovery that they have G6PDD, or they eventually have a hemolytic crises. I have received countless emails from people in this category. Their health issues run from liver, heart, blindness, renal spleen and chronic yellow color to skin, to death in some cases. These problems can occur from early in life to later in life. Many families discover G6PDD runs in their family only after the needless death or serious illness, cause by G6PDD complications, of a family member.
Hemolysis
Now that we know that hemolysis varies in intensity, let’s discuss the cause of hemolysis. When a red blood cell comes into contact with an oxidative substance, an RBC with sufficient G6PD to reduce glutathione will neutralize the oxidative substance rendering it harmless. Those with G6PDD cannot reduce enough glutathione to protect RBCs from damage so, the oxidative substance destroys the RBC. It is my opinion that his happens to everyone with G6PDD, regardless of which variant they have. What is more important than variant is the degree of G6PDD the person has. One person may have more G6PD than another so that person is able to produce more reduced glutathione to protect RBCs than a person with less G6PD. For the purpose of this discussion both less G6PD and less effective G6PD are considered the same.
Legumes and Hemolysis
Now I will discuss legumes. In every contraindicated list I have ever seen, fava beans, or broad beans, are considered contraindicated for all variants of G6PDD, yet some insist that all variants of G6PDD do not exhibit favism. The definition of favism is a condition that causes hemolysis from exposure to fava beans. As of now I have never seen a research paper or other proof as to the exact chemical, or chemicals, in fava beans that cause hemolysis.
Over the past few years, some people using hemoglobin meters have shown that many other legumes also cause hemolysis to varying degrees. Again, it is my opinion that all people react to these substances, but to varying degrees depending on severity of G6PDD, health, etc, as described above.
Because low level hemolysis (or mild hemolysis) is very hard to detect, it is logical that many people believe that they are not reacting to legumes or other substances that cause low level hemolysis. But, low level hemolysis can be very dangerous over time. Our bodies must generate more RBCs to compensate for the ones that are destroyed and the destroyed RBCs must be cleaned up. This process takes resources needed for healthy bodies, consequently we are more susceptible to other diseases and they can be more severe than when we are not undergoing low level hemolysis.
Medical research is far behind when it comes to legumes and G6PDD. Because I have had so much success in stopping hemolysis by avoiding all legumes and products containing them, I recommend that
they be avoided. Hopefully, someday maybe medical research will provide us with more information concerning the exact chemicals they contain that causes hemolysis.
How to Relieve Memory Loss, Headaches and Fatigue
Memory Loss, Headaches, and Fatigue – How to Relieve
headaches, reverse memory loss, and overcome fatigue. Reasons for mineral imbalances include:
- • Stress
- • Mineral Deficient Food Supply
- • Drinking Improper Water
- • Toxic Metals and Chemicals in our Food, Water, Air, and more
- • Improper Digestion
- • Taking the Wrong Nutritional Supplements not Compatible with Your Current Body Chemistry
- • and much more!
A Slow Metabolism, which is associated with weak adrenal and thyroid activity. Slow oxidizers have high calcium and magnesium levels. Additionally, they have low sodium and potassium levels. Those with a slow oxidation rate tend to have low energy, depression, dry skin, weight gain, cravings for sweets, are prone to infections, and more.
High Levels of Cobalt, Strontium, and Tin. If your hair analysis shows high levels of cobalt, strontium, and tin. It is important you reduce your exposure and detoxification would be beneficial. Some herbs are high in cobalt. It is best you discontinue any herbs taken in dietary supplement form. Cobalt can also be found in other supplements, water, soil, and more. Strontium toxicity can interfere with normal calcium metabolism. Tin in excess interferes with iron metabolism.
Pain and Inflammation. This is revealed as a high sodium/ potassium ratio (Na/K) on your hair analysis. A high Na/K ratio increases the magnesium burn rate due to stress. Intense stress can cause magnesium deficiency. High calcium and magnesium (Ca/Mg) ratio, in addition to other indicators, does reveal a magnesium deficiency.
Causes of Memory Loss, Headaches, and Fatigue
Memory Loss
Did you know memory loss can be caused by a magnesium deficiency or other imbalances? This hair analysis reveals indicators of a magnesium deficiency, including the high calcium / magnesium (Ca/Mg) ratio.
Headaches
A sodium deficiency, toxic metals, and other imbalances can cause headaches. This hair analysis reveals a low sodium level and also heavy metal toxicity
Fatigue
Fatigue is associated with a slow metabolism. Slow oxidizers tend to have weak adrenal and thyroid activity.
Why Organic Coffee is Important?
Grown without synthetic fertilizer or artificial pesticides, herbicides, fungicides and insecticides.
Coffee is one of the most pesticide sprayed crops around the world. These chemicals are highly toxic and detrimental to human health. Organic farming also combats climate change and emitting less carbon than chemical farming.
As a bonus, organic coffee is richer in healthful antioxidants. Your health and the health of the plant both get a boost.
为什么有机咖啡很重要? 此种植不含合成肥料或人工杀虫剂,除草剂,杀菌剂和杀虫剂。
咖啡是世界各地农药喷洒最多的农作物之一。 这些化学物质毒性很大,对人体健 康有一定的伤害。 有机耕作还可以应对气候变化,减少碳排放。但化学耕作就办 不到。
作为奖励,有机咖啡富含健康的抗氧化剂。您和植物的健康都得到了提升。

Your Digestive System and How it Works.
Stomach
- Must be super acid.
- Dissolve and absorb minerals
- Release or breakdown food.
- Proteolytic enzymes ex: Pepsin helps to breakdown proteins and kill microbes. If it is not acidic enough, it willlead to acid reflux and indigestion.
- Treatment: TMG and Apple
Cider Vinegar.
Gallbladder
- Release bile acids that made by the liver.
- Neutralize the acids in stomach.
- Detoxify chemical.
- Treatment: Bile Salt
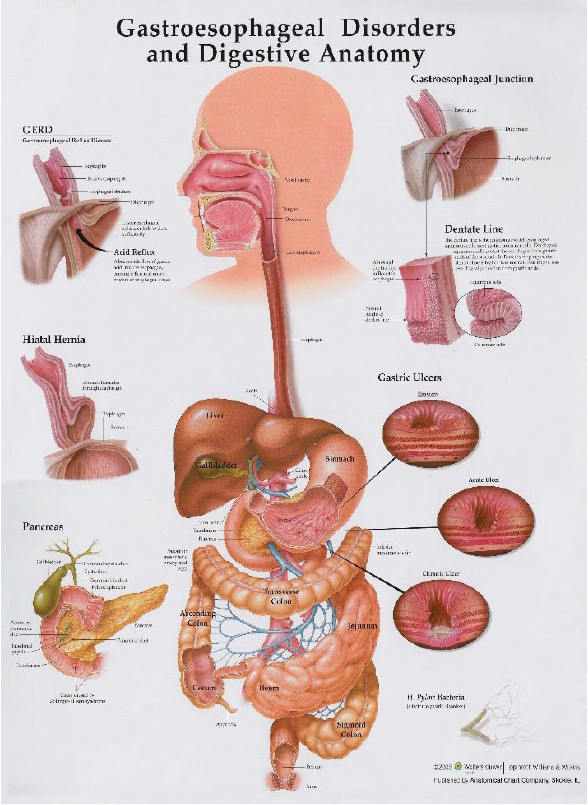
Pancreas
- Produce enzymes lipase to breakdown carbohydrates.
- When you start eating, it gives signals to brain what type of enzymes to produce and create.
- Pancreas and gallbladder work together. From very strong acid to alkaline.
Small Intestines
- 90% of digestion happens here.
- 85% of your lymphatic system is located in the small intestines and it acts to create immunity.
- 1000 trillion bacteria
- 100 trillion cells
- Good and bad bacteria in gut can adapt to the environment.
- Antibiotic is harmful to the gut because it destroys both the good and bad bacteria. They form a new strategy to survive and adapt.
- It is our second brain.
- Digestion can affect our mood-depression.
CHOLESTEROL
- Plays an important role in our body.
- 75% cholesterol is produced by our liver.
- 25% cholesterol comes from food intake.
- 2000mg of cholesterol is produced by our liver per day. 1000mg is produced by other parts of our body. We produce total 3000mg of cholesterol per day.
- Every cell require cholesterol.
- Cholesterol is needed for the production of bile, hormones, brain function, Vit D .
- High triglycerides is caused by taking too much sugar and refined carbohydrates.
- Take your Triglycerides reading divide HDL, it should be less than 2 (normal reading)
- Here is the guide line:
o < 2 normal
o > 2—5.9 poor
o > 6 very bad - It acts as a healing agent
THYROID
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. It is an autoimmune disorder in which antibodies is directed against the thyroid gland leading to chronic inflammation.
There are mainly 3 factors that affecting Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Genetic
- Intestinal permeability
o Ex: Leaky gut. It is an autoimmune disease.
o Its trigger the body not to recognize. - Food sensitivities
o Ex: Severe sensitivity to gluten.
o Can lead to toxic exposure - Other factors that can trigger the disease: chronic infection, nutrition depletion, toxic exposure, stress.
If only genetic factor, intestinal permeability and food sensitivity is not there, Hashimoto will not manifest.
If we only checking T3, T4 and TSH, 90% of the results are inaccurate. It is important to check our Thyroid Auto Antibodies to avoid undiagnosed or thyroid diseases. They are:
- Anti thyroid peroxidase
- Thyroglobulin antibody.
MAGNESIUM
- 80% heart attack patients are due to Magnesium deficiencies.
- 57% of population are Magnesium deficiencies.
An Overview: Ozonide
The Fight Against Bacteria, Fungi and Parasites by Supporting the Oxidative System in the Human Organism
12 Dec 99 by Dr. Gerhard Steidl
1. Biological Fundamentals
Modern anaerobic bacteria have descended from primitive cells that existed when the earth had an anaerobic carbon dioxide atmosphere. Later, when the process of photosynthesis transformed the atmosphere to an aerobic oxygen atmosphere, higher life-forms, which consist of aerobic oxygen-processing cells, evolved. But anaerobic bacteria, which are not dependent on oxygen, can still find environments suitable for their existence. A human organism affected by oxygen deficiency in the intestines, for example, and in tissues and organs with corresponding hypoxy provides an adequate breeding ground for such bacteria. When anaerobic bacteria and fungi established in the human organism display asymbiotic behavior, increasingly multiply and cannot be kept under control, the body’s health will invariable suffer to some degree.
2. The use of oxygen in the oxidative system
Oxygen is essential in the life of higher cells and organisms. Living beings such as humans use oxygen in three ways:
a) Oxygen is taken into the haemoglobin and transported in erythrocytes through the arteries, capillaries and membranes to the tissue cells. It is transferred to enzyme systems for the oxidation of substrates along with the release of warmth and vital energy in the mitochondria. Approximately 97% of transported oxygen is used for energy metabolism.
b) The white blood cells need approximately 3% of this energy for producing oxygen radicals, the immune system’s best weapon against foreign and asymbiotic cells.
c) The oxygen physically bound in the haemoglobin ensures that, by means of an Hb (O2)4 = Hb + 4O2 balance, the body tissue remains oxygenated. This is designed to prevent oxygen deficiency in the body tissue, which is sealed off from the air.
3. The Oxidative and Anti-oxidative system
Although oxygen is necessary for all living functions, many components of the biochemical system, such as oxidation-sensitive enzymes, for example, must be protected from excess oxygen. The endogenous cells and iron in the haemoglobin must also be protected from oxygen radicals and oxidative stress. This is the function of the anti-oxidative system which consists, among other things, of substances such as glutathione, selenium, vitamins and, above all, the enzymes peroxide dismutase and catalase. Anaerobic bacteria do not possess these enzymes and are therefore sensitive to oxygen and oxygen-rich compounds, while mammalian (including human) cells can render oxygen radicals non-toxic. A healthy, robust organism is therefore dependent on a balance between the oxidative and anti-oxidative systems.
4. Oxygen Deficiency and Its Consequences
According to books on human physiology by authors such as Thews, Mutschler and Vaupel, anaemia and sub-oxygenation have many causes and can produce unpleasant consequences because endogenous and symbiotic cells and tissue are damaged while foreign and asymbiotic cells may be promoted. Generally, one can expect symptoms such as chronic fatigue due to deficient energy metabolism or susceptibility to infection due to a weakened immune system. When normal cells are oxygen deficient, they can degenerate into tumour cells. This was proven by Warburg, who won a Nobel prize for his discovery.
Symbiotic cells are found above all in the intestinal tract, where they are responsible for converting food, which must be broken down into usable components. Much of this work done by resident bacteria that can optionally exist anaerobically, such as E.coli, by anaerobic bacteria such as bifidobacterium and bacteroides, and also by aerobic bacteria such as Lactobacillus. But if the oxygen level in the intestines, especially the lower areas of the small intestine and the large intestine, drops to absolutely zero, then colonies of purely anaerobic bacteria will definitely build up bacteria such as Clostridia, which cannot be tolerated physiologically because it generates toxic metabolic products.
When this occurs, treatment is required because a whole series of ubiquitous unphysiological (foreign, asymbiotic) germs that is, bacteria, fungi and parasites which pollute the intestines, blood, body tissue and organs with toxins can become established. Chronic constipation can create a similar effect because the contents of the intestines remain for a longer period thus producing a more favourable environment in which the unphysiological germs can multiply. Such germ and toxin pollution can cause blood poisoning, strain on the liver, excessive demand on immune cells, even psychotic syndromes to the extent of personality changes. The symptoms are at first vague and later pronounced.
5. Ozonides from Natural Vegetable Oils
5.1 Properties
Physiologically compatible ozonides are long-chained, oxygen-rich oils. They are water-free and viscous and formed from natural fatty oils such as olive oil or castor oil and oxygen in the form of ozone. By exchanging three oxygen atoms for the double bond in unsaturated fatty acids, a bactericidal and fungicidal substance is produced. Ozonide which can obviously also attack parasites. Mixed with water, ozonides produce emulsions that can be taken internally. They were already being used clinically between 1915 and 1947 in the US., for example, against wound infection in operations and against fungi, bacteria and viruses in both humans and animals. They have not been used since 1947 because antibiotics from fungus cells and synthetic biocides (sulphonamide, chlorine compounds) became available in large quantities.
For good health, the intestinal environment must be made aerobic and the basis for anaerobic germs existence completely removed. Ozonide is perfectly suited in this regard to cleansing an unphysiological, anaerobic intestinal tract. Its effectiveness is based, among other things, on its ability to keep the intestinal mucosa moist, its capillary action and its formation of emulsions. In this way, ozonide is evenly distributed throughout the intestines and its clefts, where fungal nests or bacterial foci may reside. Eliminating anaerobic, asymbiotic germs unburdens the immune system clearly a desirable effect.
5.2 Research
The world’s largest foundation for naturopathic research, the Karl and Veronica Carstens Foundation in Essen, has financed scientific research into the biochemical properties of ozonides derived from long-chained fatty acids at universities in Erlargen, Tuebingen and Mainz since 1997. The foundation’s yearbooks publish the test results. One such result shows that, while some conventional antibiotics damage the mitochondria (i.e. the powerhouses in human cells, which produce vital energy and warmth) ozonides do not. The test for mutagenity according to OECD guidelines showed that ozonides are not mutagenic. Cell culture experiments on bacteria and fungi showed that ozonides hinder the propagation of Candida, Trichophyton, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and, to a lesser degree, Aspergillus niger, which grows aerobically and which can thus resist oxygen species. Ozonide kills off Schistosoma mensori, the pathogen causing bilharzia.
5.3 Similarity of Vegetable Endoperoxides
Over the last twenty years in the USA and England, oxygenous vegetable extracts of the endoperoxide class from more than 300 plant species including many medicinal plants such as wormwood, sage, yarrow, chamomile etc have been isolated through a time-consuming procedure, their structure analyzed and their action on bacteria tested. These endoperoxides possess a ring structure similar to, yet more complicated than, that of the ozonides and all prove to be potent germicides. They presumably serve the plants in fending off foreign germs. Traditional Chinese medicine uses Artemisia annua L. effectively to treat malaria pathogens. The active agent in Artemisia annua L., identified as arteminism, is an endoperoxide.
Synthetic ozonides can be regarded as imitating natural endoperoxides because they have a similar structure and effectiveness. Humans take in endoperoxidase, which help in the battle against bacteria, fungi and parasites, when consuming raw plant food. But when the food is cooked, the endoperoxides are destroyed along with vitamins, enzymes, and other valuable elements. Ozonides are compatible with the human organism. This is understandable when one compares the structure of ozonides with those of the underlying fatty oils and the natural endoperoxides that human cells adapted to during biological evolution.
5.4 Reinforcing the germicidal effect
Ozonides can give the intestinal tract a thorough aerobic cleansing and thus remove the basis for many problematic germs’ existence. There are, however, many kinds of bacteria, fungi and parasites that have a defence mechanism against oxygen species and therefore demand a dosage of ozonides so high that it may not be physiologically tenable. Among such germs are, for example, mould fungi such as Aspergillus niger. Recourse to phytotherapy may provide a remedial measure. In books on phytotherapy as far back as the middle ages specific plants like tansy, wormwood, carne’s-bill, cloves, walnut shells and others are described as anti-inflammatory and anti-parasitic. These properties exist as much now as they did then and can be used effectively in therapy. In fighting fungi, bacteria and parasites, water and alcohol free extracts from these plants can be combined with ozonide oils. This achieves both conversion of the anaerobic regions and an increased germicidal effect.
6. Medicinal Uses
Many people who have an infectious disease are potential beneficiaries. Ozonides can be used externally on skin diseases (skin and nail fungus, eczema, neurodermatitis, psoriasis, itching, bed sores) on internal diseases from the head (colds, sinusitis, inflammations in the mouth and pharynx, esp. inflammation of the gums and paradontosis) down to the intestinal tract (intestinal fungi, fermentation and putrefactive foci, constipation or extremely anaerobic intestinal environments with a marked increase I Clostridia in the large intestine). In either words, they can be used wherever unphysiological bacteria, fungi and parasites are associated with the diseased condition. Symptoms such as chronic fatigue, depression, cravings, overweight, and also psychological symptoms are problems that can be traced back to intoxication produced by bacteria, fungi and parasites. Results pre and pro therapy do not allow any other conclusion.
In dentistry, the healing of gum regions inflamed with paradontosis can be observed and photographically documented with both conventional curettage and application of ozonides. Micro-organisms can even play a fatal role in cancerous diseases: 15% of cancerous diseases in the world are definitely attributable to viruses and bacteria and a further 15% are suspected of being so, according to the report at a conference of specialists in internal medicine in Wiesbaden in April 1999. Experts estimate that 7000 to 10000 people die from fungal infections in Germany every year. Doctors can gain a special advantage by mastering a bioresonance method, which enables them to detect toxic pollution in the blood, for example, and to differentiate between the various kinds of toxins. Furthermore, it helps them determine which remedy and what dosage is most appropriate for the patient. Matching results in blood and stool diagnoses with both the bioresonance method and laboratory and microbiological analyses prove that bioresonance is accurate and effective. These facts are unknown in conventional Western medicine.
3 Ways to Detox with Iodine
It’s a fact we can’t ignore: we live in a toxic world. In response to this, you have probably also heard about the importance of detoxing your body. You may have even tried cleanses for specific organs such as the gut, liver, or kidneys.
But did you know that there are certain nutrients that can “work their magic” by gently helping the body to detoxify on a daily basis? Iodine is at the top of this list of important minerals which can heal as well as cleanse.
3 Critical Ways that Iodine Can Help You Detox
#1 – Iodine Can Help Your Body Detox from “Halides” (Fluoride, Bromide & Chlorine)
Let’s get specific when it comes to the toxins that are impacting your health and the health of your loved ones. Many of the dangerous chemicals we take in from the air, water, soil, and food supply are called “endocrine disruptors.”
These endocrine disruptors include bromide, chlorine, fluoride, and their derivatives, such as perchlorate (found in jet fuel), which has a chloride component.
Conditions associated with high amounts of halides in the body include:
- ovarian cysts
- uterine fibroids2
- fibrocystic breast disease
- cancers of the uterus, ovaries, breasts, and prostate3
Endocrine disruptors like bromide4 do their damage by crowding out iodine in cellular receptor sites throughout the entire body. However, these three areas – thyroid, breasts, ovaries – are where concentrations of iodine are stored and utilized the most. Likewise, they are also the places where halides like to “hang out” most.
This is a big reason why getting enough absorbable iodine into your system every day is so important. Dangerous halides are in just about everything from drinking water to pesticides, and are also in the same category as iodine on the periodic table. This means that while halides can crowd out iodine, sufficient amounts of the right kind of iodine can gently and slowly crowd out halides as well.5
Of equal concern in our toxic world are endocrine disruptors that can come in the form of “xenoestrogens” which mimic aggressive forms of natural estrogen. Like halides, xenoestrogens such as Bisphenol A replace milder forms of estrogen in the body and are increasingly connected to breast cancer, according to a 2010 report published in the journal Hormones and Cancer, 6 among others. Iodine, on the other hand, can help flush out chemically-derived xenoestrogens.
#2 – Iodine May Chelate Some Heavy Metals Like Mercury
Iodine supplementation may help you detox from heavy metals like lead, mercury, cadmium, and aluminum. Dr. David Brownstein, author of the book Iodine: Why You Need It / Why You Can’t Live Without It and an expert in iodine, states that “Iodine is a chelator of mercury. It will bind with mercury and allow the body to release [it].”7
There is also some evidence that high levels of iodine can bind to aluminum, removing it from the body, albeit at a slower rate. Dr. West cites one study where the “results obtained following iodine supplementation revealed that in some subjects, the urine levels of mercury, lead, and cadmium increased by several-fold after just one day of supplementation. For aluminum, this increased excretion was not observed usually until after one month or more on the iodine supplementation.”
To date, studies that have been done on iodine’s chelation abilities are few and far between. It is clear from anecdotal evidence, however, that there is very likely a connection.
#3 – Iodine Boosts Your Liver and Kidneys Naturally
The major detoxification pathways of the body include the liver, the kidneys, the lymph system, and the skin. And guess what? Iodine is a major player in helping each one of these organ systems function at its best. Here’s how:
The Lymph System: Iodine deficiency is a common cause of lymphatic congestion, according to Dr. John Douillard, a global leader in the field of health and Ayurveda.9
The Liver: The thyroid and the liver are intricately connected, and iodine is a key for communication between them. The metabolic thyroid hormone thyroxine (T3) is comprised of 3 iodine molecules and is inactive when it is produced by the thyroid. It must travel to the liver to be converted to its active form, tri‐iodothyronine (T4). When any of the components of this delicate process are off, the whole mechanism suffers, and so does your vital energy and overall health!
The Kidneys: As with the liver, there is a delicate relationship between thyroid function and the kidneys, in large part mediated by iodine. Several studies have established the link between kidney disease and thyroid malfunction.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is often characterized by low T3 production. Hypothyroidism is also very common amongst CKD patients, according to a 2012 study published in the Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.11
The Skin: Did you know that iodine is a natural antiseptic? In fact, in the 1800s iodine was regularly carried in vials around the neck and used to treat mosquito bites for the prevention of disease. Iodine can be useful in fighting infection and can be used as a wound cleaner. And it’s great for wrinkles on the skin as well!
How to Help Your Body Detox With Iodine
One of the best way to get rid of toxins and help your own natural detoxification pathways is to add iodine to your diet every day. Including more iodine-rich foods to your plate is one good way.
Here are some foods that contain fairly high amounts of iodine:
- Seaweeds, such as dulce and kelp
- Berries, such as strawberries and cranberries
- Seafood and fish
- Dark leafy green vegetables
- Dairy products, like eggs and cheese
For some, if not most individuals, getting enough iodine from food alone may not be enough. The World Health Organization states that approximately 2 billion people worldwide have some form of iodine deficiency.


